Table of Contents
Fencing has always been an essential way to establish boundaries, enhance safety, and provide security. While traditional wooden or chain-link fences offer physical barriers, they often fall short in preventing determined intruders or keeping animals under control. This is where electric fences, sometimes called electronic fences, step in as a modern solution.
People searching for electric fences often want practical answers. Homeowners worry about burglars. Farmers look for cost-effective ways to control livestock. Businesses and conservationists need a balance of security and safety. This guide covers what an electric fence is, how it works, why it is useful, where it is applied, and whether it is safe.
By the end, you’ll not only understand the technology but also see why electric fences are trusted worldwide in homes, farms, and even wildlife reserves.
1. What is an Electric Fence?

An electric fence is a barrier that uses electrical energy to create a psychological deterrent. Instead of relying on brute strength, it delivers a short, sharp shock to anything that comes into contact with it. The shock is unpleasant but not harmful, teaching animals and people to avoid crossing the boundary.
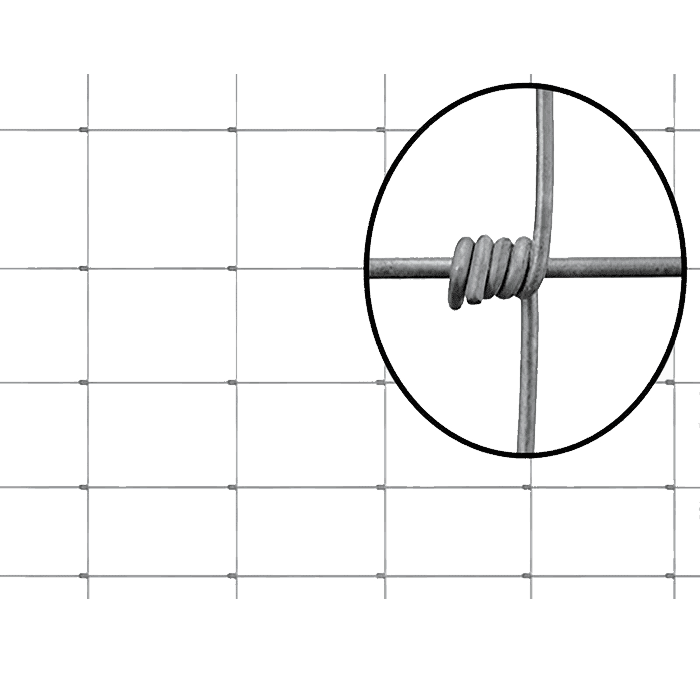
These fences typically consist of conductive wires, insulators, posts, and an energizer. The energizer sends controlled pulses of electricity through the wires, while the insulators prevent energy loss to the ground. Together, they form an efficient and cost-effective fencing solution.
Electric fences can be set up as stand-alone systems or combined with existing structures such as walls, wooden fences, or mesh panels. This flexibility allows property owners to adapt the technology to different needs without redesigning their entire perimeter.
Another important aspect is scalability. A small garden may only need a few meters of fencing, while a large ranch or industrial site may require kilometers. The same technology scales easily, making it attractive for both small and large applications.
2. How Electric Fence Works?

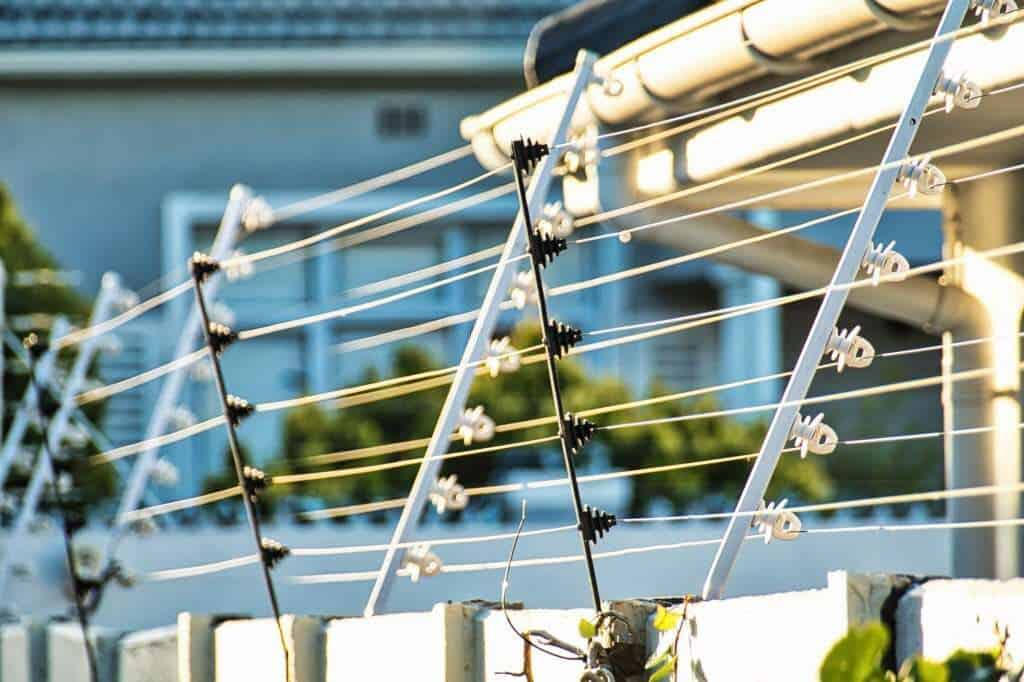
The working principle of an electric fence is simple but ingenious. At the heart of the system lies the energizer, also known as a fence charger. This device converts either mains, battery, or solar power into short bursts of high-voltage electricity.
These pulses are sent through the fence wires, which act as conductors. Unlike a continuous current, the pulses occur every second or so. This pulsing design prevents continuous contact, making the fence safe while still delivering a memorable shock.
When a person or animal touches the live wire, the electrical circuit completes through the ground. The current flows from the energizer, into the wire, through the body, and back to the ground via a grounding rod. The shock is brief but startling enough to discourage repeat contact.
Proper grounding is critical to effectiveness. Without it, the current cannot flow back to the energizer, and the fence delivers little to no shock. Many installation issues come down to poor or insufficient grounding.
Some systems include monitoring technologies. Advanced models can trigger alarms if the wires are tampered with or cut, making them suitable for high-security applications. Others integrate with smart devices, allowing property owners to check fence status remotely.
Power sources vary depending on need. In remote areas, solar-powered energizers are popular because they require no external power grid. In urban or industrial zones, mains-powered systems are preferred for reliability.
3. Why do Fences Need to be Electrified?

Traditional fences can act as physical barriers, but determined intruders or strong animals often find ways around them. Electrification adds a psychological layer of defense, making the fence far more effective. The fear of a shock often prevents people or animals from even attempting contact.
For farmers, electrification offers significant advantages. Livestock quickly learn to avoid the fence after one or two encounters. This reduces wear and tear on the fence itself, saving money on maintenance. Compared to heavy wooden or metal barriers, electric fences are cheaper and easier to move when pastures need rotation.
From a security perspective, electrified fences create an active deterrent. Unlike walls or barbed wire, which can be cut or climbed, an electric fence makes intrusion uncomfortable and risky. Even if someone tries to bypass it, the chances of triggering an alarm are high.
Another reason for electrification is flexibility. Farmers and landowners can build temporary or semi-permanent fences to manage land use. Once no longer needed, the fence can be dismantled and reused in another location.
Wildlife management also benefits. Electrified fences help protect crops from large animals such as elephants, deer, or wild boar. At the same time, they prevent livestock from escaping into forests or roads, reducing conflict between humans and animals.
Environmental benefits exist too. Since electric fences rely on psychological deterrence, they require fewer materials than traditional fencing. Less wood, less steel, and less concrete mean a lighter environmental footprint overall.
4. Application Scenarios of Electric Fence

Electric fences are not limited to one industry or purpose. They have found applications across agriculture, residential security, commercial facilities, conservation projects, and even temporary events. The adaptability of the technology makes it one of the most versatile fencing options today.
Agricultural Use
In agriculture, electric fences are invaluable. They allow farmers to contain livestock such as cattle, goats, horses, and sheep without building costly permanent enclosures. Because animals respect the fence after one or two shocks, they are less likely to damage it compared to wooden or metal barriers.
Electric fences also make rotational grazing easier. Farmers can divide large fields into smaller sections, moving animals from one area to another without needing heavy infrastructure. This improves pasture health and maximizes land productivity.
Wildlife protection is another agricultural advantage. In areas where wild animals often destroy crops, electric fences offer a non-lethal solution. Elephants, deer, and boars can be kept away without the need for dangerous traps or harmful methods.
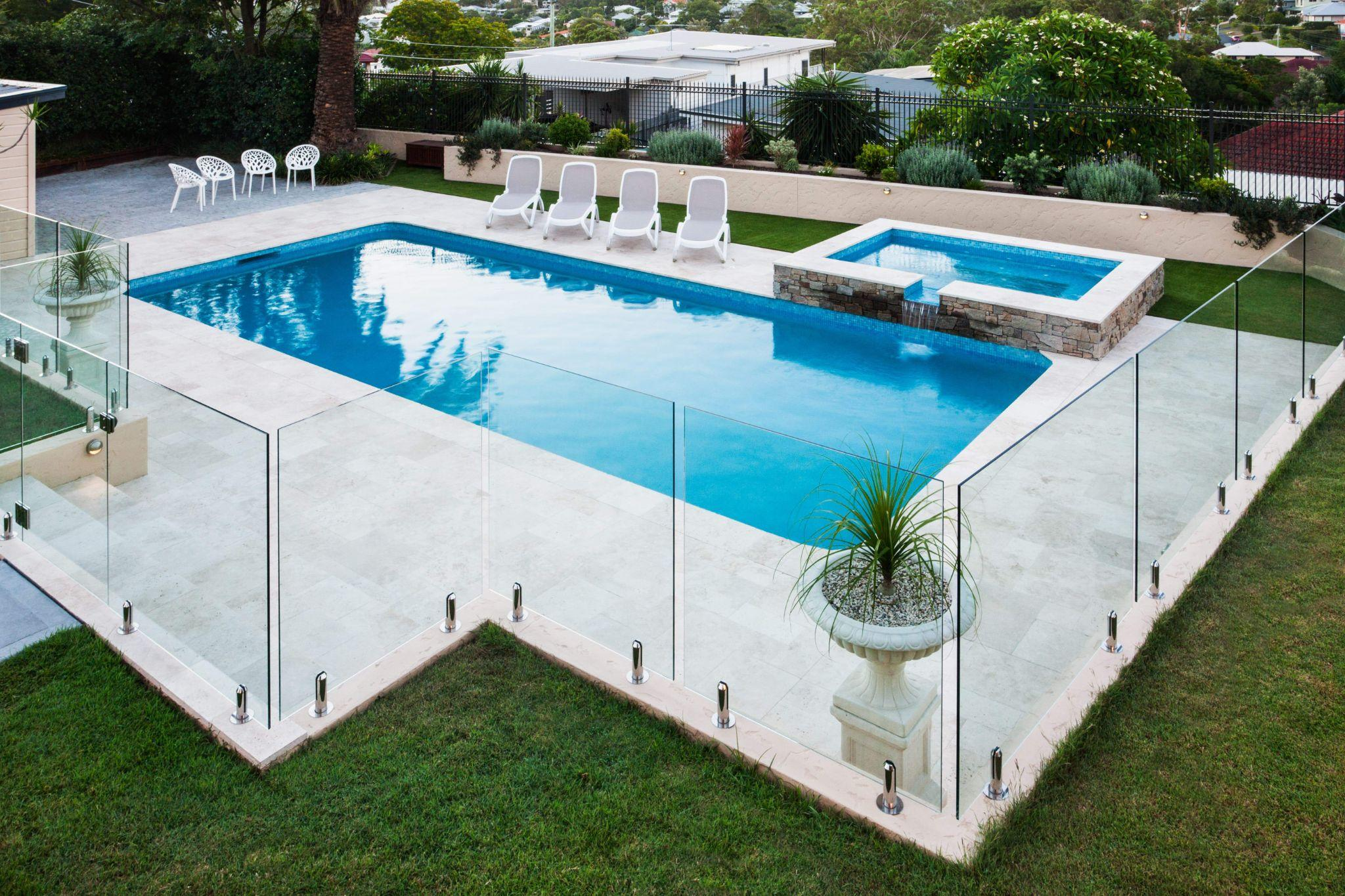
Residential Security
Homeowners use electric fences to boost perimeter security. Often mounted above walls or gates, they provide a strong deterrent to burglars. Even before touching the fence, warning signs and the visible wires discourage attempts.
Another benefit is integration with home security systems. Many residential electric fences connect to alarms, cameras, or smart devices. If the fence is tampered with, homeowners receive instant alerts, allowing them to act quickly.
Aesthetic considerations also play a role. Unlike tall concrete walls or unsightly barbed wire, modern electric fences are designed to blend with existing architecture. They protect homes without turning them into fortresses.
Industrial and Commercial Use
Industries and businesses face serious risks from theft and intrusion. Electric fences provide a cost-effective yet powerful security layer for warehouses, factories, and office compounds. By electrifying the perimeter, companies make it much harder for intruders to access valuable goods.
In high-security facilities such as airports, power stations, or military bases, electric fences often include multiple zones, alarms, and CCTV integration. These systems are highly regulated and designed to detect as well as deter.
For businesses, the financial savings are clear. Instead of hiring large numbers of guards or building massive walls, companies can rely on electric fencing as a 24/7 protection system.
Wildlife and Conservation Areas
Electric fencing plays a crucial role in conservation. It helps protect endangered species, safeguard human settlements, and balance ecosystems. For example, in Africa and Asia, electric fences are used to prevent elephants from entering villages and destroying crops.
At the same time, they help keep predators like lions or wolves out of livestock areas, reducing human-wildlife conflict. By creating controlled boundaries, conservationists can protect both animals and communities.
Another benefit is that electric fences can be moved or adjusted as needed. This makes them less invasive than permanent concrete or metal barriers, preserving natural habitats.
Temporary Events and Projects
Electric fences are also useful in temporary situations. Construction sites, concerts, festivals, or temporary livestock enclosures can all benefit from portable electric fences. These are lightweight, easy to install, and reusable.
For events, they provide crowd control while protecting valuable equipment. For construction projects, they reduce the risk of theft or accidents. Once the event or project ends, the fence can be dismantled and relocated.
Transportation and Infrastructure Protection
Electric fences are increasingly used to secure infrastructure such as railways, highways, and bridges. They prevent unauthorized access that could lead to accidents or vandalism. In some countries, electric fences are used near railway lines to stop livestock from wandering onto tracks.
Airports also rely on electric fences to protect runways and restricted areas. This keeps both wildlife and intruders away from sensitive zones, ensuring smooth operations and safety for passengers.
Correctional Facilities and Military Bases
Prisons and military bases require extremely high levels of security. Electric fences form part of layered security systems, ensuring escape attempts or unauthorized entry are met with immediate deterrence. These fences often include advanced monitoring, alarms, and integration with surveillance cameras.
The psychological barrier of a high-voltage warning is often enough to discourage attempts. In environments where safety and control are non-negotiable, electric fences provide reliable protection.
Airports and Seaports
Airports and seaports handle valuable goods and sensitive operations. Electric fences are widely deployed to prevent trespassing, cargo theft, and sabotage. Their visibility alone acts as a deterrent, while their alarm systems make it difficult for intruders to go unnoticed.
In seaports, fences also protect shipping containers, docks, and customs areas. Since these facilities often cover large areas, electric fencing provides a cost-effective way to cover kilometers of perimeter.
Renewable Energy Sites
With the growth of solar farms and wind farms, electric fences have become essential for protecting renewable energy assets. These sites often span wide open spaces in remote locations, making them vulnerable to theft and vandalism. Electric fencing helps safeguard expensive panels, turbines, and equipment.
Solar-powered energizers are especially useful in these areas, allowing fences to operate independently of the grid. This ensures continuous protection even in off-grid locations.
Sports and Recreation Facilities
Sports complexes, golf courses, and private clubs sometimes use electric fencing to protect their grounds. It prevents unauthorized access after hours and safeguards valuable turf or equipment. For golf courses, electric fences can also keep out wildlife such as deer or wild boars that might damage the greens.
5. Is Electric Fence Safe?

Safety is the most common concern when people consider electric fences. The thought of electricity running through wires naturally raises questions, especially for families with children or farms with animals.
The truth is that electric fences are specifically designed to be safe. The shock is unpleasant but non-lethal, regulated by international safety standards. Energizers limit the current and pulse duration, ensuring no long-term harm occurs.
For animals, electric fences are safer than alternatives like barbed wire, which can cause injuries, infections, or even fatalities. A brief shock teaches animals to respect the boundary without physical damage.
For humans, the fence delivers a short jolt that startles but does not injure. Children who accidentally touch it may cry from surprise but will not be harmed. Warning signs and proper installation further reduce risks.
Electric fences also allow customization. Farmers can set lower voltages for small animals and higher voltages for larger livestock or intruder deterrence. This flexibility ensures both effectiveness and humane use.
Maintenance plays a big role in safety. Regular checks on grounding, insulators, and wires prevent malfunctions. Many property owners choose professional installation to guarantee compliance with safety standards.
Modern electric fences also include additional safety measures. Some energizers automatically reduce power when the fence is touched for prolonged periods. Others are designed with built-in fault detection to prevent accidents.
In summary, when properly installed and maintained, electric fences are among the safest and most humane fencing solutions available.
Conclusion
Electric fences represent the evolution of boundary control. They combine psychology, technology, and practicality to create barriers that are both effective and humane. From farms to homes, businesses, and conservation areas, they offer unmatched versatility.
Unlike traditional fences, electric versions don’t rely solely on physical strength. Instead, they create a deterrent strong enough to discourage attempts at intrusion or escape. At the same time, they remain safe for people, animals, and the environment.
For anyone looking to secure property, manage livestock, or protect crops, an electric fence can be a smart investment. With proper installation and maintenance, it delivers long-term peace of mind at a reasonable cost.